Radiography is a technique that uses radiation to create images of objects or materials that are not visible to the naked eye. This method is widely used in various fields, from medicine to industry, to reveal internal structures and detect hidden flaws. In the medical field, radiography helps doctors visualize the inside of the human body. It's commonly used to examine bones, soft tissues, and organs, allowing for early detection of injuries or diseases. In industrial settings, radiography plays a crucial role in quality control and safety. It allows inspectors to identify defects or structural issues within materials, components, or equipment without damaging them. This non-destructive testing (NDT) method is essential for ensuring the integrity of critical infrastructure and machinery. This guide will explore the different applications of industrial radiography across various industries. If you're interested in how radiography is used in healthcare, we recommend checking out this article from the FDA. Industrial radiography is just one of many non-destructive testing methods used by professionals. To learn more about NDT, check out our comprehensive guide here. Note: Industrial radiography is also sometimes referred to as industrial radiology. Industrial radiography (IR) is a technique that uses ionizing radiation—such as gamma rays or x-rays—to inspect the internal structure of materials and components. This process enables engineers and inspectors to detect cracks, voids, corrosion, and other hidden flaws without altering the object being tested. The two most common types of radiation used in industrial radiography are gamma rays and x-rays. Both can penetrate through many materials, making it possible to perform internal inspections without disassembling or damaging the item. There are two main applications of industrial radiography: Industries like aerospace, automotive, energy, and construction rely heavily on radiography to maintain high-quality standards. For example, aircraft manufacturers use it to test engine parts and fuselage joints, while oil and gas companies use it to inspect pipelines and storage tanks. Related read: What Is a Dosimeter and Why Is It Important? One of the key advantages of industrial radiography is that it’s a non-destructive testing (NDT) method. This means that the material being tested remains intact after the inspection, unlike destructive testing methods that require sampling or modification. For instance, if you want to test for lead in paint, you might apply a chemical reagent that changes color upon contact with lead. This method is destructive because it alters the paint permanently. In contrast, radiography leaves the material untouched, making it ideal for ongoing monitoring and quality assurance. While industrial radiography is a powerful tool, it involves exposure to ionizing radiation, which can be harmful if not handled properly. The sources of radiation include both radioactive materials and x-ray machines. Due to the potential risks, strict safety protocols and regulations are in place. Industrial radiographers must undergo specialized training and follow detailed procedures to minimize exposure to themselves and others. In fact, industrial radiography is known to have more incidents involving radiation than other types of work with radioactive materials. Compliance with safety laws is mandatory, especially in countries like the U.S., where the Nuclear Regulatory Commission oversees the use of radiography equipment. Radiographic testing involves using radiation to inspect an object’s internal structure. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the process: The images produced during radiographic testing are called radiographs. Traditionally, these were captured on film, but modern systems now use digital detectors for faster and more accurate analysis. Industrial radiography relies on two main types of radiation: x-rays and gamma rays. Each type requires different equipment and has unique characteristics. Gamma ray radiography uses radiation emitted from a radioactive source contained within the equipment. This makes it compact and portable, suitable for use in tight spaces. However, since it cannot be turned off, it requires proper shielding to protect workers from unnecessary exposure. X-ray equipment is typically larger and more powerful, making it ideal for use in factories, warehouses, and other large environments. Unlike gamma ray devices, x-ray machines can be turned on and off, which enhances safety when not in use. Due to the risks associated with radiation, the use and transportation of radiography equipment require special licenses. In the U.S., the Nuclear Regulatory Commission regulates these activities. If you're considering a career in industrial radiography, there are several steps you need to take: Industrial radiographers are responsible for conducting inspections using x-rays or gamma rays to detect flaws in materials, components, and structures. They often work on large, stationary assets like pipelines, boilers, and pressure vessels, requiring them to travel to various job sites. They analyze the resulting radiographs to determine the integrity of the inspected items and ensure compliance with safety and quality standards. According to ZipRecruiter, the average annual salary for an industrial radiographer in the U.S. is around $54,000. However, salaries can vary significantly depending on location, experience, and additional certifications. Obtaining additional certifications, such as those related to specific types of equipment or industries, can increase earning potential and open up more job opportunities. Certification is required in most regions to practice industrial radiography. The process usually includes hands-on training, a radiation safety course, and a written exam. Common certifications include: Each state or country may have its own specific certification requirements, so it’s important to research local regulations. While drones are not yet widely used in industrial radiography, their potential is growing. One company, Pacific Imaging, has developed a drone equipped with an x-ray imaging system called DroneX. It is currently used to inspect power line conductor sleeves, reducing the need for manual inspections that can be dangerous. As drone technology continues to advance, we may see more applications of radiography using aerial platforms. This could revolutionize how inspections are conducted, especially in hard-to-reach or hazardous environments. Mounting Magnets,Round Base Magnets,Rotatable Hook Magnet,Rare Earth Mounting Magnets Anfeng Industrial Co.,Ltd , https://www.afmagnets.comWhat Is Industrial Radiography Used For?
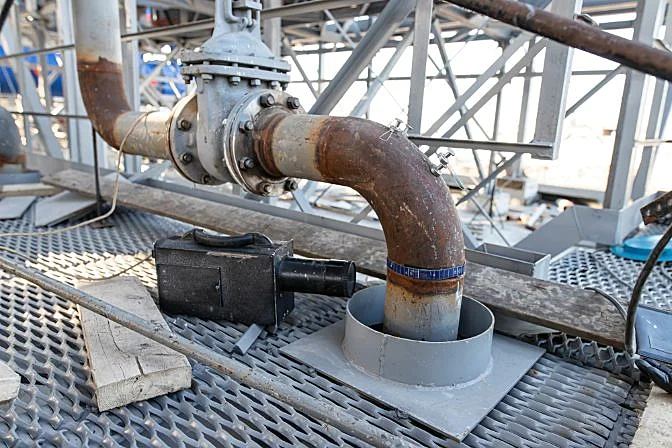 Radiographic testing used on a pipe
Radiographic testing used on a pipeUnderstanding Industrial Radiography
 An industrial boiler
An industrial boilerNon-Destructive vs. Destructive Testing
Safety Considerations in Industrial Radiography
How Does Radiographic Testing Work?
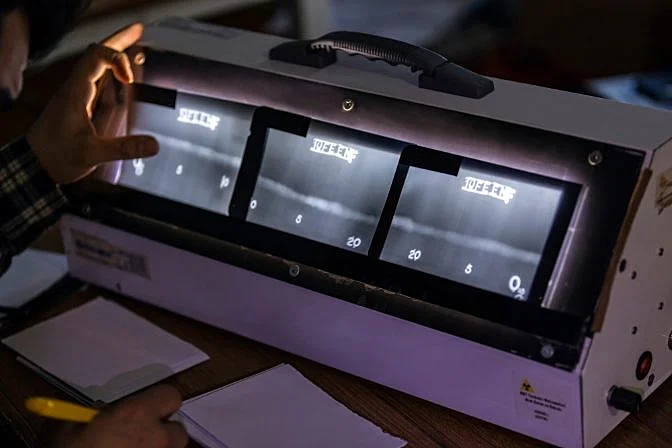

Industrial Radiography Equipment
Gamma Ray Equipment
X-Ray Equipment
Industrial Radiographer Careers and Salaries
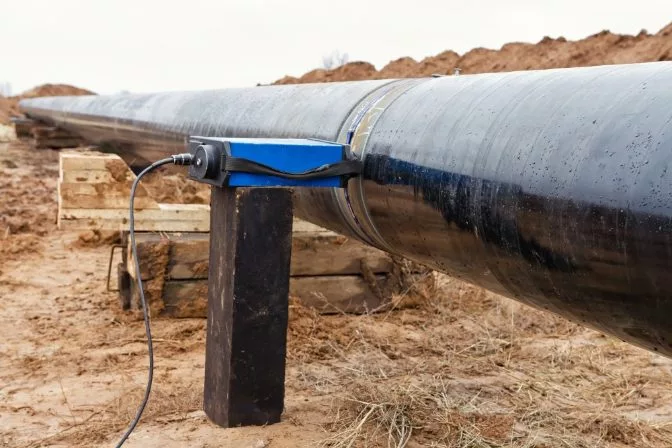 Radiographic testing used on a weld in an aboveground pipe
Radiographic testing used on a weld in an aboveground pipeIndustrial Radiography Certification
Drones and Industrial Radiography
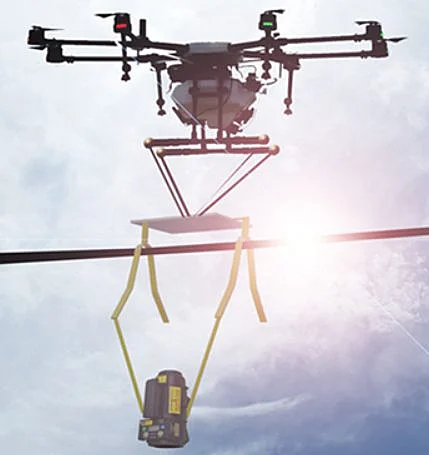 Photo credit: Pacific Imaging
Photo credit: Pacific Imaging