
The surprisingly long history of electric cars
While electric vehicles (EVs) have only recently begun to challenge the dominance of internal combustion engines, their history dates back more than a century. This journey has been marked by innovation, setbacks, and eventual resurgence.
At the turn of the 20th century, there were actually more electric vehicles on the road than gasoline-powered cars. However, this changed with the rise of the Ford Model T and the widespread availability of gasoline. Despite this, EVs remained a niche market for decades.
The 21st century brought a new wave of interest in electric mobility. Companies like Tesla and Nissan introduced affordable and efficient electric cars, paving the way for a global shift towards sustainable transportation. Today, electric vehicles are no longer just a novelty—they’re a major force in the automotive world.
Electric car history timeline
The evolution of electric vehicles can be broken down into several key periods: from the early experiments of the 1800s to the modern-day electric revolution. Each phase reflects the technological advancements and societal shifts that have shaped the industry.
First electric cars (1830-1880)
Throughout the early 1800s, inventors across Europe and the United States experimented with electric propulsion. These early prototypes, though limited in range and speed, laid the groundwork for the development of practical electric vehicles.
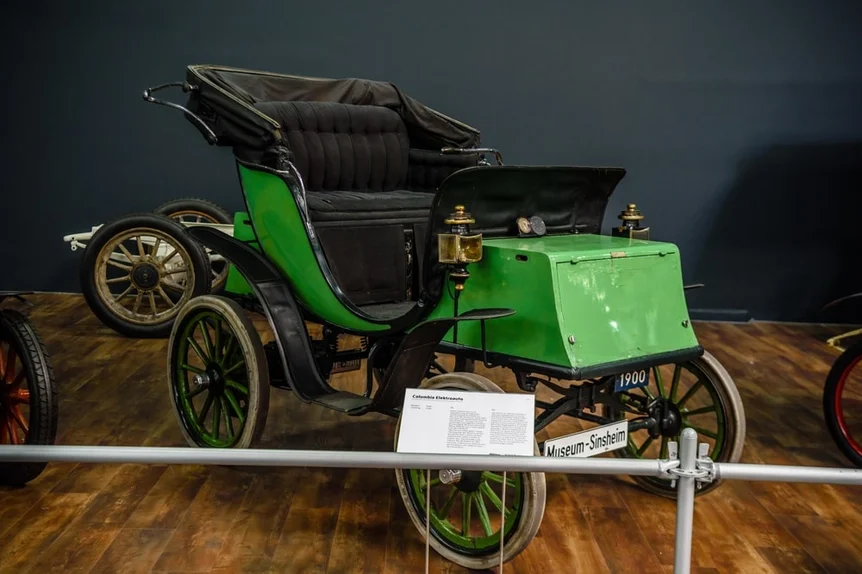

When was the first electric car made?
Some of the earliest electric vehicles were built in the 1830s, with inventors like Robert Anderson and Sibrandus Stratingh creating small-scale models. However, it wasn’t until the late 1880s that electric vehicles became more practical, thanks to advances in battery technology.
Who made the first electric car?
William Morrison is often credited with building the first practical electric car in the 1890s. His vehicle, based on a horse-drawn carriage, could carry up to 12 passengers and reached speeds of around 20 mph.
What was the first electric car?
Morrison’s electric carriage was one of the earliest examples of a fully functional electric vehicle. It demonstrated the potential of electric propulsion and inspired further innovation in the field.
The transition to motorized transport (1880-1914)
As the 20th century approached, electric vehicles gained popularity, especially in urban areas where electricity was more accessible. However, they faced competition from steam and gasoline-powered cars, which eventually dominated the market.
Who invented the internal combustion engine?
Gottlieb Daimler and Carl Benz are widely recognized as the inventors of the first internal combustion engine vehicles. Their work in the 1880s helped establish gasoline as the dominant fuel source for automobiles.
When did hybrid cars come out?
Hybrid vehicles, which combine electric and gasoline power, began to emerge in the early 20th century. Porsche developed one of the first hybrid cars, while Thomas Edison and Henry Ford also explored the concept of electric vehicles.
The rise of the internal combustion engine (1914-1970)
With the mass production of gasoline-powered cars, electric vehicles gradually lost ground. The affordability and convenience of gasoline made it the preferred choice for most drivers, leading to a decline in the use of electric cars.
By the mid-20th century, electric vehicles had nearly disappeared from the market. However, their legacy lived on, inspiring future generations of engineers and inventors who would eventually bring them back into the mainstream.
The return of electric vehicles (1970-2003)
The 1970s saw renewed interest in electric vehicles due to rising oil prices and growing environmental concerns. Automakers like General Motors and NASA explored alternative fuel technologies, laying the groundwork for the next generation of electric cars.

The launch of the Toyota Prius in 1997 marked a significant milestone in the development of hybrid vehicles. Its success paved the way for the broader acceptance of electric and hybrid cars in the automotive industry.
Going electric (2003-2020)
The early 2000s saw the emergence of companies like Tesla, which aimed to make electric vehicles more powerful and appealing to a wider audience. The release of the Tesla Roadster in 2008 demonstrated the potential of electric cars to compete with traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.

Nissan’s introduction of the Leaf in 2010 further accelerated the adoption of electric vehicles. With its zero-emission design and affordability, the Leaf became one of the best-selling electric cars in the world.
The tipping point of EV growth (2021 and beyond)
By 2021, electric vehicles had reached a critical point in their development. Sales continued to grow rapidly, with over 10 million electric cars sold worldwide in 2022 alone. This growth is expected to continue as more countries implement policies to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable transportation.

Norway leads the world in electric vehicle adoption, with nearly 80% of new cars sold being electric. Other countries, including the UK, Germany, and China, are also making significant progress in transitioning to electric mobility.
The future of electric cars
The future of electric vehicles looks bright. With continued investment in research and development, as well as the expansion of charging infrastructure, electric cars are becoming more accessible and practical for everyday use.
As governments set ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions and consumers increasingly favor sustainable options, the demand for electric vehicles is expected to grow even further. The road ahead is filled with opportunities, and electric mobility is set to play a central role in shaping the future of transportation.





